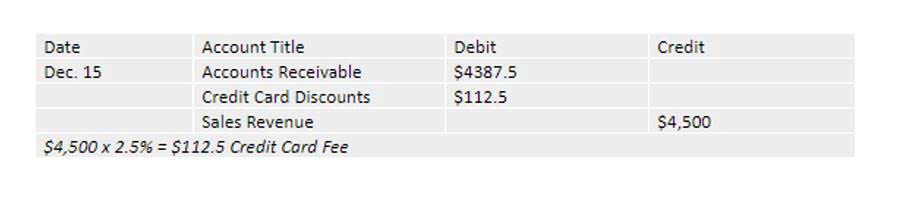
However, these methods only represent a small portion of the available MCDM methods. In future research, it would be valuable to explore and examine a broader range of MCDM methods to determine their potential applicability in specific cases. For instance, the ELECTRE method can be particularly helpful in outranking alternatives without compensation, which could prove interesting in cases where stakeholders are seeking a consensus solution (Figueira et al. 2016). Examining the TOPSIS (Lai et al. 1994) and VIKOR (Mardani et al. 2016) methods is also interesting, as these methods, along with ELECTRE, PROMETHEE, and AHP, are often discussed collectively what are retained earnings for their potential applicability (Opricovic, 1998).

Identify alternatives
To achieve this, surveys can be conducted to gather opinions from a larger group of stakeholders (C1, C3, C4, C7, C9, C12, C13, C30, C35, C36, C39, C42, C44, C48, C51, C61, C66), potentially extending to mass participation. In this roundup, we’ve gathered six time-tested tools, frameworks and principles for making high-quality decisions at fast-moving startups. They include strategies for distilling the information needed to make a decision, testing potential solutions and reconciling clashing perspectives. We hope they’ll help take the dread out of decision-making and lend you clarity on choices that can drive your startup forward. The 1950s can generally be thought of as the beginning of concrete decision-making frameworks since this is when organizations began using statistical tools for their decision models. In particular, data quality was considered anew in order to distinguish measurements based on optimal solutions from those based on real-world solutions.
- The types of stakeholder groups vary across different fields, and when citizens are incorporated into the MAMCA process, the decision-making becomes more delicate.
- The versatility of MAMCA is evident in the range of available weight elicitation methods and MCDM techniques it accommodates.
- They must champion its use, communicate its importance, and lead by example, demonstrating its application in real business scenarios.
- It can be concluded that an important added value of the MAMCA methodology, which makes it unique in comparison to other MCDA methods, is therefore often overlooked.
- While we generally recommend against aggregating scores from different stakeholder groups into a single unified metric, certain contexts, such as enterprise evaluation, necessitate a final assessment for the alternatives.
This is how effective teams navigate the decision-making process
Additional time and effort must be invested to ensure that this particular stakeholder group’s perspectives are thoroughly considered and integrated (Renn et al. 2013). Involving citizens typically leads to an increase in the number of representatives, aligning with MAMCA’s objectives. The aim is not merely to include public opinions but to comprehensively account for their preferences and empower them as genuine decision-makers in the evaluation process. Engaging citizens as active participants fosters a more inclusive decision-making process, which can potentially lead to greater acceptance and satisfaction with the outcomes (Cooper & Wood, 1974; Fagence, 2014). Moreover, citizen involvement can contribute valuable local knowledge, diverse perspectives, and innovative ideas to the process, resulting in more robust and well-informed solutions (Stivers, 1990; Callahan, 2007; Chopyak & Levesque, 2002). Thus, expanding the role of citizens in MAMCA is not only beneficial for the decision-making result but also helps create a more engaged and informed decision-making process.
- Read on for how Rajaram uses the SPADE framework to help synchronize and speed up collaboration over difficult choices.
- These methodologies can be incorporated into specific stages or applied across multiple stages, as needed.
- Decision-making frameworks, such as the Cynefin framework and the Eisenhower Matrix, offer structured approaches to tackle complex decisions.
- This ensures that decisions are not made against significant objections or concerns and fosters a sense of ownership and accountability among stakeholders.
- However, the feasibility of implementing these methods ultimately depends on the specific case at hand.
- “We used it for our most important initiatives and we actually would always start out by defining the ‘A’ first.
- Reducing and simplifying frameworks will help you keep your practice lean and effective.
Evaluating Decisions
- “If you’re responsible for the decision, meet with that individual, explain the decision, and get buy-in.
- We confirm enrollment eligibility within one week of your application for CORe and three weeks for CLIMB.
- Anytime you are faced with an important decision, it is essential not to let biases get in your way.
- Our easy online enrollment form is free, and no special documentation is required.
The three steps of Stage (I), as well as step (E) MCGDM of Stage (II) are essential to perform in decision making framework every context where the method is applied. The other steps are optional, and the approach can differ, related to the envisioned engagement goal. Always remember to consider the possibility of not making a decision or doing nothing and be aware that both options are actually potential solutions in themselves. Instituting an accountability system from the very beginning can help startups avoid bigger traps down the line.
Encouraging open communication, active listening, and fostering a culture of collaboration can help navigate through such challenges. Furthermore, embracing a mindset of adaptability and flexibility can be crucial when faced with uncertainty. By acknowledging that not all https://www.bookstime.com/ variables can be controlled or predicted, decision-makers can focus on building resilience and agility within their frameworks to respond effectively to unexpected developments. A major decision with far-reaching impacts deserves some fixation and perfectionism.
The 5 main decision-making models
Innovative business models are at the core of strategic adaptation in the face of disruption. The future of decision-making in leadership now demands a balance between human intuition and machine intelligence, with an increasing emphasis on change management and adaptation to disruption. This Technology’s influence on strategic decision-making foreshadows a future where trust, access, and integration will become critical components of competitive advantage. The integration of autonomy and artificial intelligence in decision-making processes is not only inevitable but is also setting new standards for efficiency.
Overcoming Challenges in Decision-Making Frameworks

Unlike the rational framework, intuitive decision-making relies on gut instincts and past experiences. It involves making decisions based on intuition and can be particularly useful in situations where time is limited or information is scarce. Here are 6 structured decision-making models for businesses to make effective decisions to minimize risks, optimize resources, and achieve sustainable growth. The factor 8 process is a process of change, starting with creating awareness, followed by identifying solutions at different level (Macharis, 2022). Actor involvement, possible by means of MAMCA, allows then to see what will be the impacts of these solutions on the objectives of the actors that are influenced or can be influenced. The participatory evaluation process allows to come to better and better supported solutions that enable to accelerate the transition.
